Artificial Intelligence
Creating The AssemblyLine For KnowledgeWorkers
Generative AI made waves this year, from DALL-E-2 to ChatGPT. These tools are
improving the productivity of knowledge workers—~2x in the case of AI coding
assistants.
AI training cost declines continued at an annual rate of 70%, the cost to train a large
language model to GPT-3 level performance collapsing from $4.6 million in 2020 to
$450,000 in 2022..We expect cost declines to continue at a 70% rate through2030.
AI should increase the productivity of knowledge workers more than 4-foldby 2030.At
100% adoption, AI could increase global labor productivity ~$200 trillion, dwarfing
the ~$32trillion intotalknowledgeworker salaries.
The effects of Artificial Intelligence in everyday life are rising, whether we are
aware of it or not.The impact of AI will be seen in almost every industry around the
globe. Indeed, that includes physicians, attorneys, and others.
Software engineerscompleted a coding taskin lessthan half the time with AI codingassistant GitHub Copilot.
According to a research,AI can createa graphic designfor just$0.08** in minutes —adi minimiscost comparedto $150for human labor.
Advanced Battery Systems
Enabling Autonomous Mobility systems that collapses the cost
Declining costs of Advanced Battery Technology should cause an explosion in form factors, enabling Autonomous
Mobility systems that collapse the cost of getting people and things from place to place. Electric drivetrain cost
declines should unlock micro-mobility and aerial systems, including flying taxis, enabling business models that
transform the landscape of cities. Autonomy should reduce the cost of taxi, delivery, and surveillance by an order of
magnitude, enabling frictionless transport that will increase the velocity of e-commerce and make individual car
ownership the exception rather than the rule. These innovations combined with large-scale stationary batteries should
cause a transformation in energy, substituting electricity for liquid fuel and pushing generation infrastructure
towards the edge of the network.
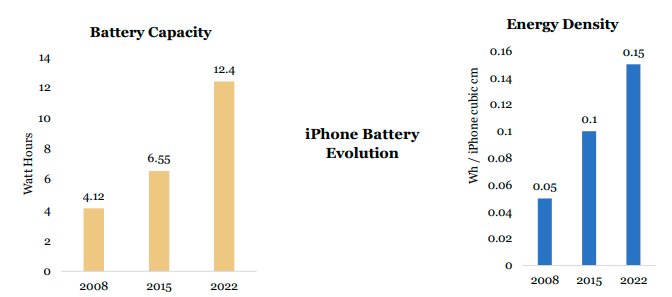
- ▪ Improvements in battery capacity and energy density will be critical to advances in intelligent devices.
- ▪ To preserve battery life, the first four versions of Apple’s smartwatch displays powered off unless wearers raised their wrists.
- • Satellite connectivity providers like Iridium and Starlink have made worldwide connectivity a reality by taking advantage of the cost declines in re-usable rockets.

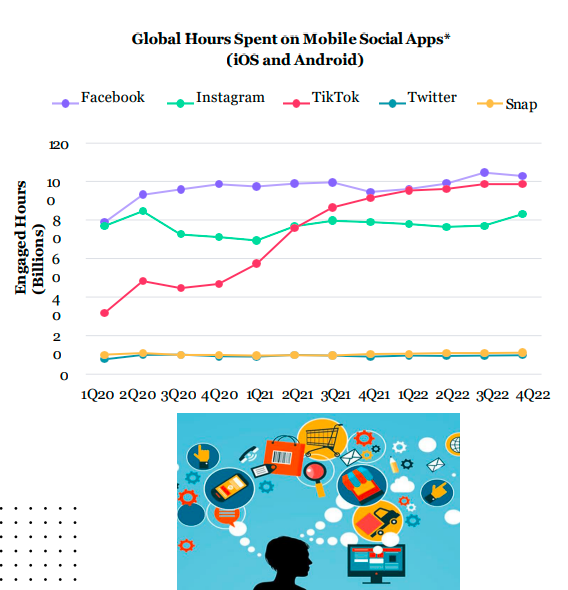
Digital Consumers
Global Hours Spent on Mobile Social Apps* (iOS and Android)
Transitioning To Online Leisure
- • In 2022, digital leisure spending* totaled $6.6 trillion and, during the next eight years, should grow 17% at a compound annual rate to $22.5 trillion adjusted for inflation. Four trends should contribute to its growth:
- • Connected TV (CTV): Roughly 85% of US households have access to at least one CTV, but the CTV ad market is only 23% the size of total US TV ad budgets. In our view, CTV is at an inflection point and will take share from both linear TV and other digital ad budgets.
- • New Social Platforms: Nearly 40% of Gen Z consumers prefer to search on TikTok and Instagram over Google Search and Maps. Social platforms with the best recommendation engines should command the majority of ad budgets, with content-based social media likely outperforming follow-and-feed social media.
- • Sports Betting: Despite macro headwinds, consumer demand for sports betting remains strong. Legalization of online/mobile sports betting should continue to catalyze growth.
- • Gaming: The convergence of video games and social media should sustain gaming revenue growth. Video games should provide end-to-end virtual entertainment that rivals physical experiences.
- • According to research, global consumers spent 21% of their $31 trillion leisure budget on digitally-facilitated goods and services in 2022. Demand for digital goods and services is likely to grow 17% at an annual rate in real terms, surpassing demand for physicallyfacilitated goods and services in 2029
- • As the gaming industry transitions to full-service virtual worlds, video games and social media could merge as consumers socialize and entertain in game-supported virtual spaces, at the expense of physical environments. According to research, the convergence between gaming and social media should boost the growth in gaming revenue from 7% at a compound annual rate during the past five years to 10% during the next five years.
Digital Wallet
Disintermediating Traditional Banking
- • Having onboarded billions of consumers and millions of merchants, digital wallets could transform the economics associated with traditional payment transactions, saving them nearly $50 billion in costs.
- • With 3.2 billion users, digital wallets have penetrated 40% of the global population. Research suggests that the number of digital wallet users will increase 8% at an annual rate, penetrating 65% of the global population by 2030.
- • As consumers and merchants adopt digital wallets, the usage of traditional checking accounts, credit and debit cards, and direct merchant accounts should decline, disrupting traditional payment intermediaries.
- • Cutting out middlemen, digital wallets could facilitate closed-loop transactions for more than 50% of their payment volumes, potentially adding $450 billion to the current $1 trillion in digital wallet enterprise value by 2030. In 2021, digital wallets facilitated 49% of e-commerce transactions, up from 18% in 2016. Since 2016, digital wallets have been gaining share at the expense of credit cards, bank transfers, and cash.
- • In 2021, digital wallets facilitated 29% of offline transactions, nearly double the 16% in 2018. Overtaking cash as the primary means of offline transactions during the COVID pandemic in 2020, digital wallets continue to gain share.
- • After acquiring billions of users, digital wallets are onboarding millions of merchants to platforms that enable direct consumer-merchant transactions that disintermediate traditional financial institutions.
Payment MethodsAsShare Of Global E-Commerce Volume

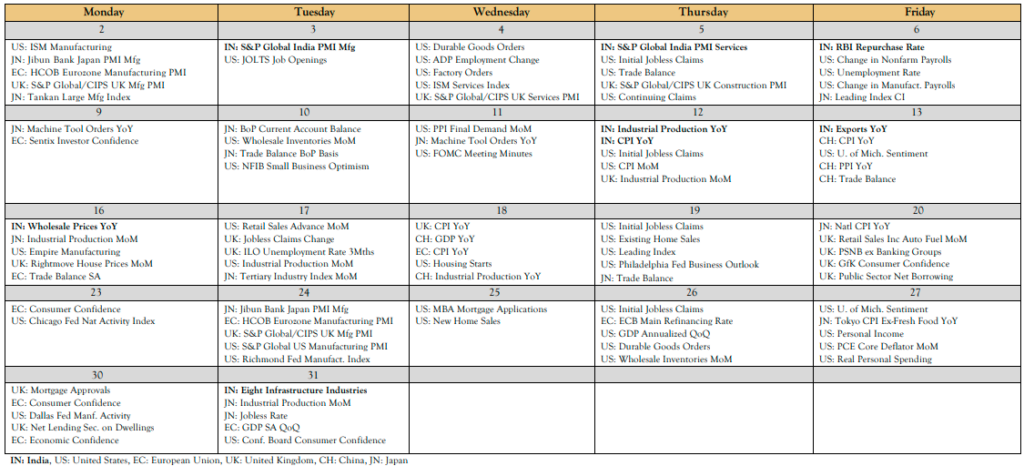
World Economic Calender
Semiconductors
GainingTraction In The Midst Of Crisis
The future of the semiconductor industry will be shaped by a range of disruptive themes, with AI chips
being one of the themes that will have a significant impact on semiconductor companies.
AI systems need to process massive amounts of data quickly. While the performance of generalpurpose chips has improved enough to kick-start a new generation of AI technology, they cannot keep
up with the exponential increase in the volume of data that AI systems process. As a result, chip design
emphasis has shifted from a race to place more transistors onto a square millimeter of silicon to focus
on building microprocessors as systems, made up of multiple components, each of which is designed to
perform a specialized task.
As the tech industry’s customer base consolidates, it designs more and more of its own chips and sends
them straight to foundries for manufacture. This is partly because merchant market suppliers have
disappointed when it comes to delivering sufficiently powerful, power-efficient chips to support AI
workloads, and partly because these companies want to gain a proprietary edge with their tech stack.
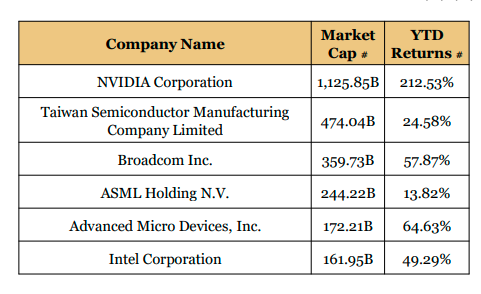
Insights from Top Ranked Companies
Nvidia
Nvidia has dominated the GPU market for years. In May 2020, Nvidia unveiled its next-generation GPU technology called Ampere, which will become the foundation for its AI strategy and product portfolio. Ampere features the third generation of Tensor Core, a chip that’s purpose-built for accelerating AI. The A100 GPU is the first AI accelerator based on the Ampere architecture and will offer unified support for training and inference. On the software front, Nvidia unveiled Jarvis, a new
application framework for building conversational AI services. In September 2020, Nvidia announced plans to acquire UK-based chipmaker Arm for $40bn.
Intel
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co., or TSMC, is the world’s largest contract manufacturer of the semiconductor chips—otherwise known as integrated circuits, or just chips—that power our phones, laptops, cars, watches, refrigerators and more. Its
clients include Apple, Intel, Qualcomm, AMD and Nvidia. The $550 billion firm today controls more than half the global market for made-to-order chips and has an even tighter stranglehold on the most advanced processors, with more than 90% of market share by some estimates. The scarcity of chips has thrust TSMC from a largely anonymous services company to the center of a global tussle over the future of technology; the firm will play an outsize role in determining what the world looks like at the end of this decade.
Datafication
Creating The Potential For Super-Exponential Growth
The term “datafication” refers to the process of turning various aspects of our lives, activities, and interactions into digital data. This data can then be collected, analyzed, and utilized to gain insights, make informed decisions, and optimize processes. The rise of datafication has been a significant trend driven by advancements in technology, particularly in areas such as the Internet of Things (IoT), big data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning.
Here are some key points to understand about the rise of datafication:
- • Data generation: With the proliferation of digital devices, sensors, and online platforms, a vast amount of data is generated every day. This data includes information about user behavior, preferences, locations, interactions, transactions, and more.
- • IoT and connected devices: The Internet of Things has played a crucial role in datafication. Everyday objects are now embedded with sensors and connected to the internet, enabling the collection of real-time data. Examples include smart thermostats, wearable fitness trackers, connected cars, and smart home appliances.
- • Business insights: Datafication has transformed how businesses operate. Companies can analyze customer data to understand buying patterns, preferences, and trends. This information can be used to tailor marketing strategies, improve products, and enhance customer experiences.
- • Healthcare and wellness: Wearable devices and health apps track individual health metrics, providing users and healthcare professionals with valuable insights into fitness levels, sleep patterns, and overall well-being
- • Urban planning and smart cities: Datafication contributes to the development of smart cities, where data is used to optimize transportation systems, energy consumption, waste management, and public services.
- • Data analytics and AI: Advanced data analytics techniques, including machine learning and AI, play a crucial role in making sense of the vast amounts of data generated through datafication. These technologies can uncover patterns, correlations, and insights that were previously difficult to identify
- • Decision-making: Datafication enhances decision-making across various sectors. Businesses can make informed choices based on data-driven insights. Governments can use data to inform policies, and individuals can make better choices informed by personal data.
While datafication offers numerous benefits, it also raises important concerns. Data privacy, security, and ethical considerations are paramount, as the collection and use of personal data raise questions about how information is stored, shared, and protected. Also, the widespread use of data raises ethical concerns related to consent, data ownership, and potential biases in algorithms. Striking a balance between data utilization and protecting individual rights is a significant challenge.
Electric Vehicles
DefyingThe Skeptics With Exponential Growth
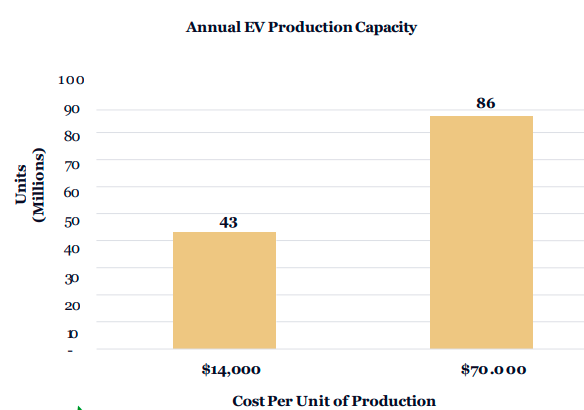
- • At a historical auto industry capital efficiency of $14,000 per unit capacity, the annualized ~$600 billion earmarked for EV investment would equate to 43 million units in annual production per year. If all automakers were to realize the capital efficiency associated with EVs, $600 billion would accommodate 86 million units, approaching total auto production today.
- • By 2027, auto buyers probably will conclude that used cars or new EVs will make more economic sense than new ICE vehicles. If so, the drop in ICE vehicle sales could set in motion a death spiral for many incumbent automakers. In response to falling prices, consumers could delay EV purchases or purchase used cars at the expense of new internal combustion cars.
- • EV charging rate is a good proxy for overall performance, capturing the efficiency, range, and power capabilities of the system. In the past four years, charging rates have improved nearly three-fold, from 40 to 15 minutes for 200 miles of range. During the next five years, it could drop nearly four-fold to 4 minutes.
- • If research forecasts for 2027 are correct, EV unit sales will scale at 50% during the next five years, from roughly 7.8 units million in 2022 to 60 million units in 2027.

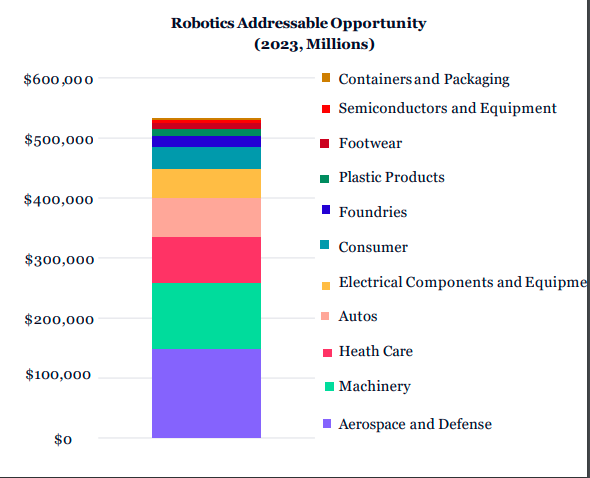
Robotics & 3D Printing
Promoting A Manufacturing Revolution
- • Robotics and 3D printing can collapse time from development to production, shorten supply chain footprints, reduce waste, and lower costs.
- • Research estimates that manufacturing robots and 3D printing could scale at a ~80% annual rate during the next eight years, from $70 billion in 2022 to ~$9 trillion by 2030.
- • The adoption of industrial robots accelerated after the 2002 dot-com bust and again after the 2008-2009 crisis. The responses to the China/US trade conflict in 2019 and supply chain bottlenecks from 2020 through 2022 have been the same.
- • Advances in computer vision and deep learning have increased the performance of robots
- • Amazon is producing ~1,000 robots per day. Within the next few years, it could add more robots than employees per year.
- • 3D printing is likely to enable new products and markets. Boston Dynamics’ Atlas humanoid robot, for example, achieved a strength-to-weight ratio that enabled leaps and somersaults, thanks to 3D printing.
- • 3D printing costs should be compared to those over the lifetime of a part—from design to retirement—in traditional manufacturing. While upfront costs can be higher, 3D printed parts can be produced much faster with more durability than parts manufactured traditionally.
- • Doctors use patient-specific 3D printed models to pre-plan surgeries and customize 3D printed tools/surgical guides for procedures, shortening operating room time and improving patient outcomes.
- • Across a range of surgeries, 3Dprinted tools, guides, and models reduced operating time on average by ~30% and increased performance, measured by surgical accuracy and results, on average by ~40-50%.

Orbital Aerospace
Edit Column Enabling Global Connectivity
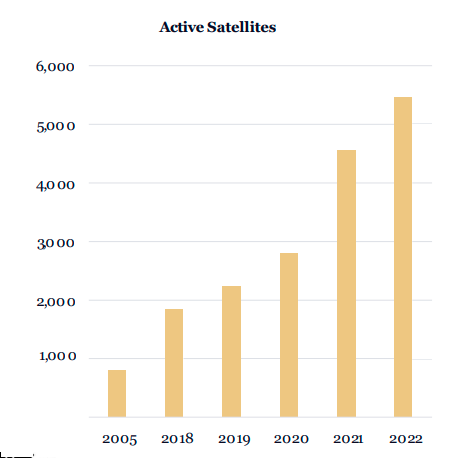
- • Aerospace costs are declining, thanks to advancements in deep learning, mobile connectivity, sensors, 3D printing, and robotics. As a result, satellite launches and rocket landings are proliferating.
- • In the coming decade, satellite broadband and hypersonic flight could generate annual revenues of ~$84 billion and ~$270 billion, respectively.
- • SpaceX put an end to soaring launch costs with its Falcon 9 reusable rocket. Falcon 9 has flown the same booster 14 times. Thanks to reusable rockets, SpaceX nearly doubled its launches to 61 rockets in 2022.
- • Thanks primarily to its rapid turnaround time, the first stage of the Falcon 9 costs less than $1 million to refurbish, according research model. In contrast, each Space Shuttle launch cost ~$1.5 billion.
- • While satellites launched into geostationary orbit (GEO) technically offered global coverage, latency limited a compelling broadband internet experience. Today, companies are launching thousands of low-cost satellites into low earth orbit (LEO) and enabling continuous global coverage with low latency and direct-to-mobiledevice connectivity.
- • Since 2004, the cost of satellite bandwidth has dropped 7,500-fold, from $300,000,000 to $40,000/ Gigabits per second (Gbps). Thanks to Starship, costs could fall another 40-fold to ~$1,000/Gbps during the next five years. According to research, 1 Gbps can serve 200 customers at a capital cost of ~$1,000/Gbps, SpaceX could recoupitsStarshipinvestment with a one-time chargeof $5per customer.
Indian Industry Looks Forward to a RecordBreaking Future
Introduction
Over the past few years, India’s industrial landscape has witnessed a noteworthy evolution characterized by a dynamic transition towards embracing innovation and adopting advanced technologies. This transformation has positioned the country as a prominent destination for international enterprises, owing to its highly skilled workforce, cost-efficient operations, and a government that actively supports this shift. Consequently, India is now asserting itself as a significant participant in the worldwide business arena, presenting promising avenues for B2B alliances and cooperative ventures.
Tech-Manufacturing Boom
Since the 1980s, businesses across the globe have been outsourcing various services such as software
development, customer support, and business process management to India. With the increasing competitiveness in global labor markets and the growing popularity of distributed work models, India’s role as the world’s outsourcing destination has gained renewed momentum. In the next decade, it is anticipated that the number of individuals employed in India for overseas jobs will experience substantial growth, potentially doubling to exceed 11 million.
Furthermore, India is on the verge of emerging as a global manufacturing powerhouse. This transformation is being facilitated by corporate tax reductions, government incentives, and significant investments in
infrastructure, all of which are driving capital inflow into the manufacturing sector. Recognizing the
substantial potential of a globally competitive manufacturing industry to stimulate economic growth and employment, the Indian government is actively promoting and supporting this sector.
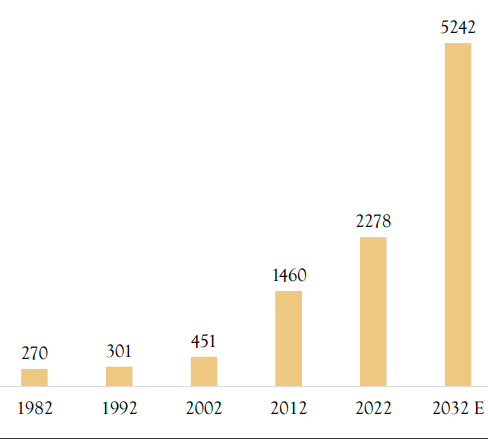
Country’s electronics manufacturing journey
PLI Scheme
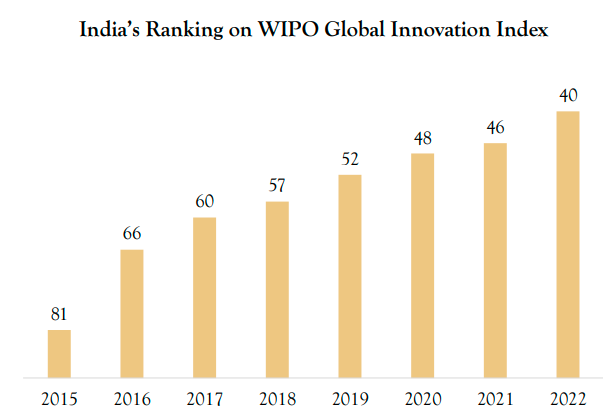
India’s Ranking on WIPO Global Innovation Index
With a strong emphasis on advanced technology, the Indian government initiated a Production Linked Incentive scheme in the fiscal year 2021-22. This program is aimed at bolstering local manufacturing across 14 strategic sectors, including automotive manufacturing and components, specialized steel, electronics, batteries,
pharmaceuticals, electric vehicles, and drones. In addition to this, a separate fund of $10 billion was allocated to encourage domestic production of semiconductors and display systems. Currently, India relies entirely on imports to meet its semiconductor requirements. Deloitte forecasts that the Indian semiconductor market will reach a value of $55 billion by 2026, with a significant portion, over 60%, being driven by three key industries:
smartphones and wearables, automotive components, and computing and data storage. In 2022, the Semicon India program was introduced, inviting semiconductor companies to establish and operate their manufacturing facilities in India. Both international and
domestic players have responded positively to this initiative. Moreover, New Delhi has eased regulations to position India as a prominent hub for drone manufacturing by the year 2030. The country has emerged as the second-largest mobile phone manufacturer in the world with more than 200 mobile phone manufacturing units having been set up on its soil. With some commodities gaining aspirational value and an increase in discretionary spending, this decade is poised to bring major market opportunities for global players to
enter India and leverage its markets along with its young demography.